Matplotlib Slider Widget:交互式数据可视化的强大工具
Matplotlib是Python中最流行的数据可视化库之一,而Slider Widget是其中一个强大的交互式工具。本文将深入探讨Matplotlib Slider Widget的使用方法、应用场景以及高级技巧,帮助您充分利用这一功能,创建动态、交互式的数据可视化作品。
1. Matplotlib Slider Widget简介
Matplotlib Slider Widget是一个交互式控件,允许用户通过滑动条来动态调整图表中的参数。这个功能非常适合用于探索数据、演示数学概念或创建交互式数据可视化应用。
以下是一个简单的Slider Widget示例:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.widgets import Slider
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
plt.subplots_adjust(bottom=0.25)
t = np.arange(0.0, 1.0, 0.001)
a0 = 5
f0 = 3
s = a0 * np.sin(2 * np.pi * f0 * t)
l, = plt.plot(t, s, lw=2)
ax.set_xlabel('Time (s)')
ax.set_ylabel('Amplitude')
ax.set_title('how2matplotlib.com: Simple Sine Wave')
ax_freq = plt.axes([0.25, 0.1, 0.65, 0.03])
slider_freq = Slider(ax_freq, 'Frequency', 0.1, 30.0, valinit=f0)
def update(val):
freq = slider_freq.val
l.set_ydata(a0 * np.sin(2 * np.pi * freq * t))
fig.canvas.draw_idle()
slider_freq.on_changed(update)
plt.show()
Output:

在这个例子中,我们创建了一个正弦波图表,并添加了一个滑动条来调整频率。用户可以通过移动滑动条来实时改变正弦波的频率。
2. Slider Widget的基本结构
Slider Widget主要由以下几个部分组成:
- 图形对象(Figure)和轴对象(Axes)
- Slider对象
- 更新函数
- 事件连接
让我们详细了解每个部分:
2.1 创建图形和轴对象
首先,我们需要创建一个图形对象和轴对象:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
plt.subplots_adjust(bottom=0.25) # 为滑动条留出空间
# 在这里绘制初始图形
ax.plot([0, 1, 2, 3, 4], [0, 1, 4, 9, 16], label='how2matplotlib.com')
ax.set_xlabel('X-axis')
ax.set_ylabel('Y-axis')
ax.set_title('how2matplotlib.com: Quadratic Function')
ax.legend()
这段代码创建了一个基本的图形,我们将在此基础上添加Slider Widget。
2.2 创建Slider对象
接下来,我们创建Slider对象:
from matplotlib.widgets import Slider
ax_slider = plt.axes([0.25, 0.1, 0.65, 0.03])
slider = Slider(ax_slider, 'Parameter', 0, 10, valinit=5)
这里,我们定义了滑动条的位置、标签、范围和初始值。
2.3 定义更新函数
更新函数是Slider Widget的核心,它定义了当滑动条值改变时应该执行的操作:
def update(val):
# 获取滑动条的当前值
param = slider.val
# 更新图形
ax.clear()
ax.plot([0, 1, 2, 3, 4], [0, param, param*4, param*9, param*16], label='how2matplotlib.com')
ax.set_xlabel('X-axis')
ax.set_ylabel('Y-axis')
ax.set_title(f'how2matplotlib.com: Quadratic Function (a={param:.2f})')
ax.legend()
# 重绘图形
fig.canvas.draw_idle()
2.4 连接事件
最后,我们需要将更新函数与滑动条的值变化事件连接起来:
slider.on_changed(update)
plt.show()
这样,每当滑动条的值发生变化时,update函数就会被调用,从而更新图形。
3. Slider Widget的高级应用
3.1 多个滑动条
在某些情况下,我们可能需要多个滑动条来控制不同的参数。以下是一个使用两个滑动条的示例:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.widgets import Slider
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
plt.subplots_adjust(bottom=0.3)
t = np.arange(0.0, 1.0, 0.001)
a0, f0 = 5, 3
s = a0 * np.sin(2 * np.pi * f0 * t)
l, = plt.plot(t, s, lw=2)
ax.set_xlabel('Time (s)')
ax.set_ylabel('Amplitude')
ax.set_title('how2matplotlib.com: Sine Wave with Amplitude and Frequency Control')
ax_freq = plt.axes([0.25, 0.1, 0.65, 0.03])
ax_amp = plt.axes([0.25, 0.15, 0.65, 0.03])
slider_freq = Slider(ax_freq, 'Frequency', 0.1, 30.0, valinit=f0)
slider_amp = Slider(ax_amp, 'Amplitude', 0.1, 10.0, valinit=a0)
def update(val):
freq = slider_freq.val
amp = slider_amp.val
l.set_ydata(amp * np.sin(2 * np.pi * freq * t))
fig.canvas.draw_idle()
slider_freq.on_changed(update)
slider_amp.on_changed(update)
plt.show()
Output:
在这个例子中,我们使用两个滑动条分别控制正弦波的频率和振幅。
3.2 使用Slider控制颜色
Slider不仅可以用于控制数值参数,还可以用于调整颜色。以下是一个使用Slider控制颜色的示例:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.widgets import Slider
from matplotlib.colors import rgb_to_hsv, hsv_to_rgb
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
plt.subplots_adjust(bottom=0.3)
x = np.linspace(0, 10, 100)
y = np.sin(x)
line, = ax.plot(x, y, lw=2)
ax.set_xlabel('X-axis')
ax.set_ylabel('Y-axis')
ax.set_title('how2matplotlib.com: Color Control with Slider')
ax_hue = plt.axes([0.25, 0.1, 0.65, 0.03])
ax_saturation = plt.axes([0.25, 0.15, 0.65, 0.03])
ax_value = plt.axes([0.25, 0.2, 0.65, 0.03])
slider_hue = Slider(ax_hue, 'Hue', 0, 1, valinit=0.5)
slider_saturation = Slider(ax_saturation, 'Saturation', 0, 1, valinit=1)
slider_value = Slider(ax_value, 'Value', 0, 1, valinit=1)
def update(val):
h = slider_hue.val
s = slider_saturation.val
v = slider_value.val
rgb = hsv_to_rgb((h, s, v))
line.set_color(rgb)
fig.canvas.draw_idle()
slider_hue.on_changed(update)
slider_saturation.on_changed(update)
slider_value.on_changed(update)
plt.show()
Output:
这个例子展示了如何使用三个滑动条来控制线条的颜色,分别对应HSV颜色空间的色相、饱和度和亮度。
3.3 动态更新数据
Slider Widget还可以用于动态更新数据源。以下是一个示例,展示如何使用滑动条来控制显示的数据范围:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.widgets import Slider
# 生成示例数据
np.random.seed(0)
x = np.linspace(0, 100, 1000)
y = np.cumsum(np.random.randn(1000))
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
plt.subplots_adjust(bottom=0.25)
line, = ax.plot(x, y)
ax.set_xlabel('X-axis')
ax.set_ylabel('Y-axis')
ax.set_title('how2matplotlib.com: Dynamic Data Range')
ax_slider = plt.axes([0.25, 0.1, 0.65, 0.03])
slider = Slider(ax_slider, 'Data Range', 10, 100, valinit=100, valstep=1)
def update(val):
data_range = int(slider.val)
ax.clear()
ax.plot(x[:data_range], y[:data_range])
ax.set_xlabel('X-axis')
ax.set_ylabel('Y-axis')
ax.set_title(f'how2matplotlib.com: Dynamic Data Range (n={data_range})')
fig.canvas.draw_idle()
slider.on_changed(update)
plt.show()
Output:
在这个例子中,滑动条控制显示的数据点数量,允许用户动态调整数据范围。
4. Slider Widget的样式定制
Matplotlib提供了多种方法来定制Slider Widget的外观。以下是一些常用的样式定制技巧:
4.1 更改滑动条颜色
我们可以通过设置Slider的color参数来改变滑动条的颜色:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.widgets import Slider
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
plt.subplots_adjust(bottom=0.25)
t = np.arange(0.0, 1.0, 0.001)
a0 = 5
f0 = 3
s = a0 * np.sin(2 * np.pi * f0 * t)
l, = plt.plot(t, s, lw=2)
ax.set_xlabel('Time (s)')
ax.set_ylabel('Amplitude')
ax.set_title('how2matplotlib.com: Customized Slider Color')
ax_freq = plt.axes([0.25, 0.1, 0.65, 0.03])
slider_freq = Slider(ax_freq, 'Frequency', 0.1, 30.0, valinit=f0, color='lightgreen')
def update(val):
freq = slider_freq.val
l.set_ydata(a0 * np.sin(2 * np.pi * freq * t))
fig.canvas.draw_idle()
slider_freq.on_changed(update)
plt.show()
Output:
在这个例子中,我们将滑动条的颜色设置为浅绿色。
4.2 自定义滑动条样式
我们还可以更进一步,自定义滑动条的各个部分的样式:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.widgets import Slider
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
plt.subplots_adjust(bottom=0.25)
t = np.arange(0.0, 1.0, 0.001)
a0 = 5
f0 = 3
s = a0 * np.sin(2 * np.pi * f0 * t)
l, = plt.plot(t, s, lw=2)
ax.set_xlabel('Time (s)')
ax.set_ylabel('Amplitude')
ax.set_title('how2matplotlib.com: Highly Customized Slider')
ax_freq = plt.axes([0.25, 0.1, 0.65, 0.03])
slider_freq = Slider(
ax_freq, 'Frequency', 0.1, 30.0,
valinit=f0,
valstep=0.1,
color='lightblue',
initcolor='none'
)
slider_freq.handle.set_facecolor('red')
slider_freq.handle.set_edgecolor('black')
slider_freq.track.set_facecolor('lightgray')
def update(val):
freq = slider_freq.val
l.set_ydata(a0 * np.sin(2 * np.pi * freq * t))
fig.canvas.draw_idle()
slider_freq.on_changed(update)
plt.show()
在这个例子中,我们自定义了滑动条的轨道颜色、滑块颜色和边框颜色。
5. Slider Widget的实际应用场景
Slider Widget在许多实际应用中都非常有用。以下是一些常见的应用场景:
5.1 数学函数可视化
Slider Widget非常适合用于数学函数的可视化和教学。以下是一个二次函数可视化的例子:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.widgets import Slider
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
plt.subplots_adjust(bottom=0.35)
x = np.linspace(-10, 10, 1000)
a, b, c = 1, 0, 0
y = a * x**2 + b * x + c
line, = ax.plot(x, y)
ax.set_xlabel('X-axis')
ax.set_ylabel('Y-axis')
ax.set_title('how2matplotlib.com: Quadratic Function Visualization')
ax_a = plt.axes([0.25, 0.15, 0.65, 0.03])
ax_b = plt.axes([0.25, 0.1, 0.65, 0.03])
ax_c = plt.axes([0.25, 0.05,0.65, 0.03])
slider_a = Slider(ax_a, 'a', -5, 5, valinit=a)
slider_b = Slider(ax_b, 'b', -10, 10, valinit=b)
slider_c = Slider(ax_c, 'c', -10, 10, valinit=c)
def update(val):
a = slider_a.val
b = slider_b.val
c = slider_c.val
y = a * x**2 + b * x + c
line.set_ydata(y)
ax.set_ylim(min(y), max(y))
fig.canvas.draw_idle()
slider_a.on_changed(update)
slider_b.on_changed(update)
slider_c.on_changed(update)
plt.show()
Output:
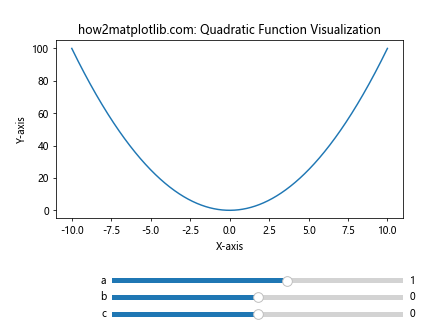
这个例子允许用户通过滑动条调整二次函数 f(x) = ax^2 + bx + c 的参数 a、b 和 c,实时观察函数图像的变化。
5.2 数据过滤和探索
Slider Widget 也可以用于数据过滤和探索。以下是一个使用滑动条过滤数据的例子:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.widgets import Slider
# 生成示例数据
np.random.seed(0)
x = np.random.randn(1000)
y = np.random.randn(1000)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
plt.subplots_adjust(bottom=0.25)
scatter = ax.scatter(x, y, alpha=0.5)
ax.set_xlabel('X-axis')
ax.set_ylabel('Y-axis')
ax.set_title('how2matplotlib.com: Data Filtering with Slider')
ax_slider = plt.axes([0.25, 0.1, 0.65, 0.03])
slider = Slider(ax_slider, 'Filter Threshold', 0, 3, valinit=1.5)
def update(val):
threshold = slider.val
distances = np.sqrt(x**2 + y**2)
mask = distances < threshold
scatter.set_offsets(np.column_stack((x[mask], y[mask])))
fig.canvas.draw_idle()
slider.on_changed(update)
plt.show()
Output:
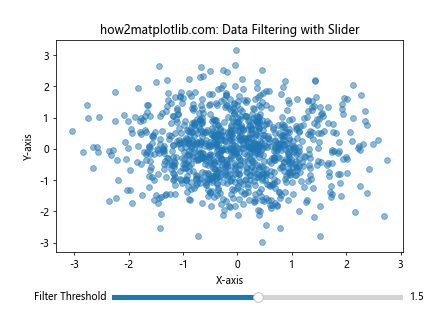
在这个例子中,滑动条控制数据点到原点的距离阈值,只显示距离小于阈值的点。
5.3 图像处理
Slider Widget 在图像处理中也有广泛应用。以下是一个使用滑动条调整图像亮度的例子:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.widgets import Slider
# 创建一个示例图像
image = np.random.rand(100, 100)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
plt.subplots_adjust(bottom=0.25)
im = ax.imshow(image, cmap='gray')
ax.set_title('how2matplotlib.com: Image Brightness Adjustment')
ax_slider = plt.axes([0.25, 0.1, 0.65, 0.03])
slider = Slider(ax_slider, 'Brightness', 0.1, 2.0, valinit=1.0)
def update(val):
brightness = slider.val
im.set_data(np.clip(image * brightness, 0, 1))
fig.canvas.draw_idle()
slider.on_changed(update)
plt.show()
Output:
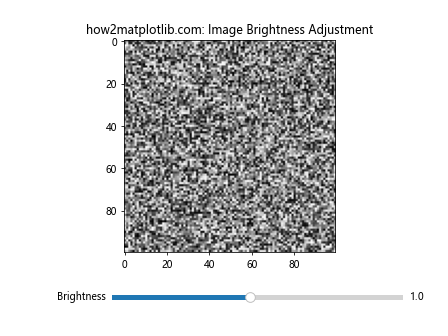
这个例子展示了如何使用滑动条来调整图像的亮度。
6. Slider Widget 的高级技巧
6.1 动态更新滑动条范围
有时,我们可能需要根据某些条件动态更新滑动条的范围。以下是一个示例:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.widgets import Slider, Button
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
plt.subplots_adjust(bottom=0.35)
t = np.arange(0.0, 1.0, 0.001)
a0 = 5
f0 = 3
s = a0 * np.sin(2 * np.pi * f0 * t)
l, = plt.plot(t, s, lw=2)
ax.set_xlabel('Time (s)')
ax.set_ylabel('Amplitude')
ax.set_title('how2matplotlib.com: Dynamic Slider Range')
ax_freq = plt.axes([0.25, 0.1, 0.65, 0.03])
slider_freq = Slider(ax_freq, 'Frequency', 0.1, 30.0, valinit=f0)
ax_button = plt.axes([0.8, 0.025, 0.1, 0.04])
button = Button(ax_button, 'Extend')
def update(val):
freq = slider_freq.val
l.set_ydata(a0 * np.sin(2 * np.pi * freq * t))
fig.canvas.draw_idle()
def extend(event):
current_max = slider_freq.valmax
slider_freq.valmax = current_max * 2
ax_freq.set_xlim(slider_freq.valmin, slider_freq.valmax)
fig.canvas.draw_idle()
slider_freq.on_changed(update)
button.on_clicked(extend)
plt.show()
Output:
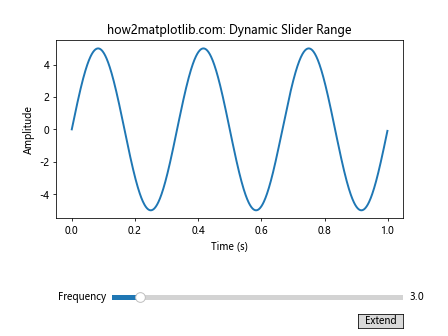
在这个例子中,我们添加了一个按钮,点击后可以将滑动条的最大值翻倍。
6.2 使用多个图形和滑动条
有时,我们可能需要在一个窗口中显示多个图形,并使用滑动条控制它们。以下是一个示例:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.widgets import Slider
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(2, 1, figsize=(8, 10))
plt.subplots_adjust(bottom=0.25)
t = np.arange(0.0, 1.0, 0.001)
a0 = 5
f0 = 3
s1 = a0 * np.sin(2 * np.pi * f0 * t)
s2 = a0 * np.cos(2 * np.pi * f0 * t)
l1, = ax1.plot(t, s1, lw=2)
l2, = ax2.plot(t, s2, lw=2)
ax1.set_xlabel('Time (s)')
ax1.set_ylabel('Amplitude')
ax1.set_title('how2matplotlib.com: Sine Wave')
ax2.set_xlabel('Time (s)')
ax2.set_ylabel('Amplitude')
ax2.set_title('how2matplotlib.com: Cosine Wave')
ax_freq = plt.axes([0.25, 0.1, 0.65, 0.03])
slider_freq = Slider(ax_freq, 'Frequency', 0.1, 30.0, valinit=f0)
def update(val):
freq = slider_freq.val
l1.set_ydata(a0 * np.sin(2 * np.pi * freq * t))
l2.set_ydata(a0 * np.cos(2 * np.pi * freq * t))
fig.canvas.draw_idle()
slider_freq.on_changed(update)
plt.show()
Output:
这个例子展示了如何使用一个滑动条同时控制两个不同的图形。
6.3 结合其他交互式工具
Slider Widget 可以与其他 Matplotlib 交互式工具结合使用,如 Button、RadioButtons 等。以下是一个结合 Slider 和 RadioButtons 的例子:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.widgets import Slider, RadioButtons
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
plt.subplots_adjust(left=0.3, bottom=0.25)
t = np.arange(0.0, 1.0, 0.001)
a0 = 5
f0 = 3
s = a0 * np.sin(2 * np.pi * f0 * t)
l, = plt.plot(t, s, lw=2)
ax.set_xlabel('Time (s)')
ax.set_ylabel('Amplitude')
ax.set_title('how2matplotlib.com: Waveform Generator')
ax_freq = plt.axes([0.25, 0.1, 0.65, 0.03])
slider_freq = Slider(ax_freq, 'Frequency', 0.1, 30.0, valinit=f0)
ax_radio = plt.axes([0.05, 0.7, 0.15, 0.15])
radio = RadioButtons(ax_radio, ('Sine', 'Cosine', 'Square'))
def update_freq(val):
freq = slider_freq.val
func = wave_funcs[radio.value_selected]
l.set_ydata(a0 * func(2 * np.pi * freq * t))
fig.canvas.draw_idle()
def update_func(label):
freq = slider_freq.val
func = wave_funcs[label]
l.set_ydata(a0 * func(2 * np.pi * freq * t))
fig.canvas.draw_idle()
wave_funcs = {
'Sine': np.sin,
'Cosine': np.cos,
'Square': lambda x: np.sign(np.sin(x))
}
slider_freq.on_changed(update_freq)
radio.on_clicked(update_func)
plt.show()
Output:
这个例子展示了如何结合使用 Slider 和 RadioButtons 来创建一个简单的波形发生器。
7. Slider Widget 的性能优化
在处理大量数据或复杂计算时,Slider Widget 的性能可能会成为一个问题。以下是一些优化建议:
7.1 使用 blitting
Blitting 是一种优化技术,可以显著提高动画的性能。以下是一个使用 blitting 的例子:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.widgets import Slider
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
plt.subplots_adjust(bottom=0.25)
t = np.arange(0.0, 1.0, 0.001)
a0 = 5
f0 = 3
s = a0 * np.sin(2 * np.pi * f0 * t)
l, = plt.plot(t, s, lw=2)
ax.set_xlabel('Time (s)')
ax.set_ylabel('Amplitude')
ax.set_title('how2matplotlib.com: Optimized Slider with Blitting')
ax_freq = plt.axes([0.25, 0.1, 0.65, 0.03])
slider_freq = Slider(ax_freq, 'Frequency', 0.1, 30.0, valinit=f0)
# 存储背景
background = fig.canvas.copy_from_bbox(ax.bbox)
def update(val):
freq = slider_freq.val
l.set_ydata(a0 * np.sin(2 * np.pi * freq * t))
# 恢复背景
fig.canvas.restore_region(background)
# 重绘线条
ax.draw_artist(l)
# 更新画布
fig.canvas.blit(ax.bbox)
slider_freq.on_changed(update)
plt.show()
Output:
这个例子使用了 blitting 技术来优化性能,特别适用于处理大量数据点的情况。
7.2 减少更新频率
在某些情况下,我们可能不需要对滑动条的每次微小变化都进行更新。我们可以通过设置一个更新阈值来减少更新频率:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.widgets import Slider
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
plt.subplots_adjust(bottom=0.25)
t = np.arange(0.0, 1.0, 0.001)
a0 = 5
f0 = 3
s = a0 * np.sin(2 * np.pi * f0 * t)
l, = plt.plot(t, s, lw=2)
ax.set_xlabel('Time (s)')
ax.set_ylabel('Amplitude')
ax.set_title('how2matplotlib.com: Reduced Update Frequency')
ax_freq = plt.axes([0.25, 0.1, 0.65, 0.03])
slider_freq = Slider(ax_freq, 'Frequency', 0.1, 30.0, valinit=f0)
last_update = 0
update_threshold = 0.1
def update(val):
global last_update
if abs(val - last_update) > update_threshold:
freq = slider_freq.val
l.set_ydata(a0 * np.sin(2 * np.pi * freq * t))
fig.canvas.draw_idle()
last_update = val
slider_freq.on_changed(update)
plt.show()
Output:
这个例子只在滑动条的值变化超过一定阈值时才更新图形,从而减少不必要的计算和重绘。
8. Slider Widget 的常见问题和解决方案
在使用 Slider Widget 时,可能会遇到一些常见问题。以下是一些问题及其解决方案:
8.1 滑动条响应延迟
问题:在处理大量数据时,滑动条可能会出现响应延迟。
解决方案:
1. 使用 blitting 技术(如前面示例所示)
2. 减少数据点数量或使用数据抽样
3. 使用异步更新
以下是一个使用异步更新的例子:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.widgets import Slider
from threading import Thread
from queue import Queue
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
plt.subplots_adjust(bottom=0.25)
t = np.arange(0.0, 1.0, 0.001)
a0 = 5
f0 = 3
s = a0 * np.sin(2 * np.pi * f0 * t)
l, = plt.plot(t, s, lw=2)
ax.set_xlabel('Time (s)')
ax.set_ylabel('Amplitude')
ax.set_title('how2matplotlib.com: Asynchronous Update')
ax_freq = plt.axes([0.25, 0.1, 0.65, 0.03])
slider_freq = Slider(ax_freq, 'Frequency', 0.1, 30.0, valinit=f0)
update_queue = Queue()
def update_plot():
while True:
freq = update_queue.get()
if freq is None:
break
new_y = a0 * np.sin(2 * np.pi * freq * t)
l.set_ydata(new_y)
fig.canvas.draw_idle()
update_thread = Thread(target=update_plot)
update_thread.start()
def update(val):
update_queue.put(slider_freq.val)
slider_freq.on_changed(update)
plt.show()
update_queue.put(None) # 停止更新线程
update_thread.join()
Output:
这个例子使用了一个单独的线程来处理图形更新,从而避免了主线程的阻塞。
8.2 滑动条范围不适合
问题:有时滑动条的默认范围可能不适合数据或用户需求。
解决方案:动态调整滑动条范围
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.widgets import Slider, Button
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
plt.subplots_adjust(bottom=0.25)
t = np.arange(0.0, 1.0, 0.001)
a0 = 5
f0 = 3
s = a0 * np.sin(2 * np.pi * f0 * t)
l, = plt.plot(t, s, lw=2)
ax.set_xlabel('Time (s)')
ax.set_ylabel('Amplitude')
ax.set_title('how2matplotlib.com: Dynamic Slider Range')
ax_freq = plt.axes([0.25, 0.1, 0.65, 0.03])
slider_freq = Slider(ax_freq, 'Frequency', 0.1, 30.0, valinit=f0)
ax_button = plt.axes([0.8, 0.025, 0.1, 0.04])
button = Button(ax_button, 'Adjust Range')
def update(val):
freq = slider_freq.val
l.set_ydata(a0 * np.sin(2 * np.pi * freq * t))
fig.canvas.draw_idle()
def adjust_range(event):
current_val = slider_freq.val
new_min = max(0.1, current_val - 10)
new_max = current_val + 10
slider_freq.valmin = new_min
slider_freq.valmax = new_max
slider_freq.ax.set_xlim(new_min, new_max)
fig.canvas.draw_idle()
slider_freq.on_changed(update)
button.on_clicked(adjust_range)
plt.show()
Output:
这个例子添加了一个按钮,允许用户根据当前值动态调整滑动条的范围。
8.3 多个滑动条之间的交互
问题:当使用多个相关的滑动条时,可能需要它们之间进行交互。
解决方案:在更新函数中处理滑动条之间的关系
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.widgets import Slider
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
plt.subplots_adjust(bottom=0.35)
t = np.arange(0.0, 1.0, 0.001)
a0, f0, p0 = 5, 3, 0
s = a0 * np.sin(2 * np.pi * f0 * t + p0)
l, = plt.plot(t, s, lw=2)
ax.set_xlabel('Time (s)')
ax.set_ylabel('Amplitude')
ax.set_title('how2matplotlib.com: Interacting Sliders')
ax_amp = plt.axes([0.25, 0.15, 0.65, 0.03])
ax_freq = plt.axes([0.25, 0.1, 0.65, 0.03])
ax_phase = plt.axes([0.25, 0.05, 0.65, 0.03])
slider_amp = Slider(ax_amp, 'Amplitude', 0.1, 10.0, valinit=a0)
slider_freq = Slider(ax_freq, 'Frequency', 0.1, 30.0, valinit=f0)
slider_phase = Slider(ax_phase, 'Phase', 0, 2*np.pi, valinit=p0)
def update(val):
amp = slider_amp.val
freq = slider_freq.val
phase = slider_phase.val
l.set_ydata(amp * np.sin(2 * np.pi * freq * t + phase))
# 调整y轴范围
ax.set_ylim(-amp*1.1, amp*1.1)
fig.canvas.draw_idle()
slider_amp.on_changed(update)
slider_freq.on_changed(update)
slider_phase.on_changed(update)
plt.show()
Output:
在这个例子中,振幅滑动条的变化会影响y轴的范围,从而保持图形始终可见。
9. Slider Widget 在科学可视化中的应用
Slider Widget 在科学可视化中有广泛的应用。以下是一些具体的例子:
9.1 物理模拟
以下是一个使用 Slider Widget 来模拟简谐运动的例子:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.widgets import Slider
from matplotlib.animation import FuncAnimation
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
plt.subplots_adjust(bottom=0.3)
t = np.linspace(0, 10, 1000)
A, k, m = 1, 1, 1
x = A * np.cos(np.sqrt(k/m) * t)
line, = ax.plot(t, x)
point, = ax.plot([], [], 'ro')
ax.set_xlim(0, 10)
ax.set_ylim(-1.5, 1.5)
ax.set_xlabel('Time')
ax.set_ylabel('Displacement')
ax.set_title('how2matplotlib.com: Simple Harmonic Motion')
ax_A = plt.axes([0.25, 0.15, 0.65, 0.03])
ax_k = plt.axes([0.25, 0.1, 0.65, 0.03])
ax_m = plt.axes([0.25, 0.05, 0.65, 0.03])
slider_A = Slider(ax_A, 'Amplitude', 0.1, 2.0, valinit=A)
slider_k = Slider(ax_k, 'Spring Constant', 0.1, 5.0, valinit=k)
slider_m = Slider(ax_m, 'Mass', 0.1, 5.0, valinit=m)
def update(val):
A = slider_A.val
k = slider_k.val
m = slider_m.val
omega = np.sqrt(k/m)
x = A * np.cos(omega * t)
line.set_ydata(x)
fig.canvas.draw_idle()
slider_A.on_changed(update)
slider_k.on_changed(update)
slider_m.on_changed(update)
def animate(i):
point.set_data(t[i], x[i])
return point,
ani = FuncAnimation(fig, animate, frames=len(t), interval=20, blit=True)
plt.show()
Output:
这个例子展示了一个简谐运动的模拟,用户可以通过滑动条调整振幅、弹簧常数和质量。
9.2 数学函数探索
以下是一个使用 Slider Widget 来探索泰勒级数逼近的例子:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.widgets import Slider
def taylor_sin(x, n):
result = 0
for i in range(n):
result += (-1)**i * x**(2*i+1) / np.math.factorial(2*i+1)
return result
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
plt.subplots_adjust(bottom=0.25)
x = np.linspace(-np.pi, np.pi, 1000)
y_true = np.sin(x)
n_terms = 1
line_true, = ax.plot(x, y_true, label='True sin(x)')
line_approx, = ax.plot(x, taylor_sin(x, n_terms), label='Taylor approximation')
ax.set_xlim(-np.pi, np.pi)
ax.set_ylim(-1.5, 1.5)
ax.set_xlabel('x')
ax.set_ylabel('y')
ax.set_title('how2matplotlib.com: Taylor Series Approximation of sin(x)')
ax.legend()
ax_slider = plt.axes([0.25, 0.1, 0.65, 0.03])
slider = Slider(ax_slider, 'Number of Terms', 1, 20, valinit=n_terms, valstep=1)
def update(val):
n = int(slider.val)
line_approx.set_ydata(taylor_sin(x, n))
fig.canvas.draw_idle()
slider.on_changed(update)
plt.show()
Output:
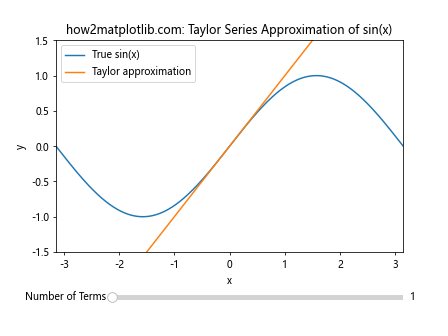
这个例子允许用户通过滑动条来调整泰勒级数的项数,从而观察近似效果的变化。
10. 结论
Matplotlib Slider Widget 是一个强大的工具,可以大大增强数据可视化的交互性和动态性。通过本文的详细介绍和丰富的示例,我们探讨了 Slider Widget 的基本用法、高级应用、性能优化技巧以及在科学可视化中的应用。
Slider Widget 不仅可以用于简单的参数调整,还可以用于复杂的数据探索、物理模拟和数学概念的可视化。通过结合其他 Matplotlib 工具,如 Button、RadioButtons 等,我们可以创建更加复杂和功能丰富的交互式可视化应用。
在实际应用中,我们需要注意性能优化,特别是在处理大量数据时。使用 blitting 技术、异步更新等方法可以显著提高 Slider Widget 的响应速度和流畅度。
总的来说,掌握 Matplotlib Slider Widget 的使用可以让我们的数据可视化作品更加生动、直观和有说服力,为数据分析和科学研究提供强有力的支持。
 极客教程
极客教程